The role of HR in manufacturing is integral to a company’s success. From managing workforce organisation and handling absences and disciplinaries, to fostering a positive culture and navigating industrial relations, HR is the foundation on which strong manufacturing businesses are built.
That said, the manufacturing industry faces several HR challenges. Research by PwC found that a staggering 92% of manufacturers cite employment costs as the key risk to their company’s growth. This finding was taken following the 2024 Autumn Budget, which introduced significant changes to employment and tax policies that will impact how companies operate this year. Additional challenges include skills shortages, fluctuating labour demands and diversity gaps.
With these obstacles in mind, how can British manufacturers stay ahead of the game? Let’s dive into 7 HR strategies that will help you thrive in the manufacturing industry in 2025.
1. Leveraging AI-enabled HR tech
Technology, cloud and artificial intelligence (AI) are seen as significant drivers of growth, with almost one third of manufacturers (29%) identifying them as opportunities for 2025. Given their potential to streamline operations and boost productivity, it’s no surprise that manufacturers are increasingly investing in AI and HR tech, using it to:
Ensure labour compliance
Manufacturing organisations can use HR software, like elementsuite, to automate essential background checks, ID verifications, and right-to-work screenings. elementsuite readily integrates with background checking tools, allowing for seamless flow of candidate information, whilst ensuring a skilled and compliant workforce on the factory floor. elementsuite also sends alerts for certification renewals and blocks workers without sufficient training from taking shifts to maintain compliance.
Empower employees with self-service capabilities
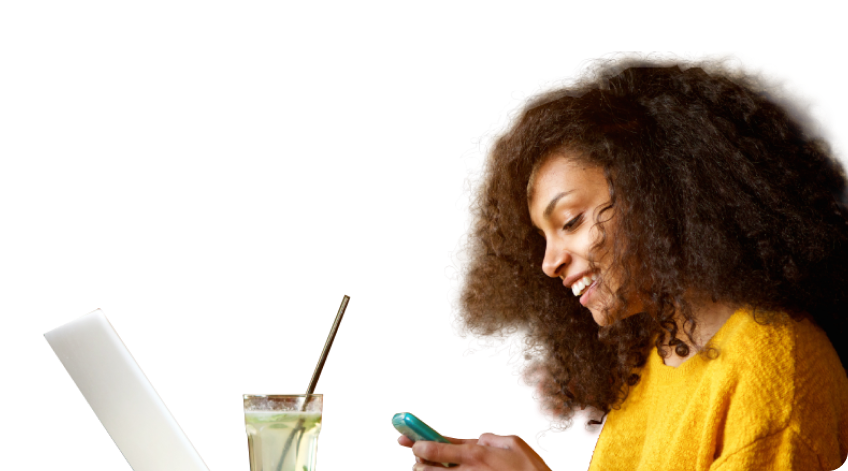
With an AI-enabled HR assistant like ELLA, employees can ask questions, check company policies and more, gaining instant answers to their HR queries, without having to wait for HR or management to respond.
Not only does this save money in terms of admin time, it hands control back to your workforce. It’s a no-brainer: your HR team gets to focus on strategic initiatives, and your employees get the tools they need to take charge of their work-life balance.
Automate repetitive tasks
To improve efficiency and save time, manufacturing companies can use HR and workforce management software to automate repetitive tasks, like screening resumes, onboarding new employees, creating schedules and processing payroll. In fact, 68% of the sector identifies enhanced productivity through automation as a crucial strategy for managing rising cost pressures.
Take automated scheduling tools, for example. These tools generate schedules based on business demand, staff requirements, employee availability, skills, and working time regulations (along with other specific company policies). What’s more, if there are any upcoming absences, swap requests, or changes to demand, you’ll be automatically notified, allowing you to quickly update the schedule and notify your team in good time.
2. Building a skilled manufacturing workforce in the UK
The British manufacturing sector is facing a significant skills shortage. As of September 2024, there were 61,000 manufacturing job vacancies in the UK.
But why are UK manufacturers struggling to recruit the talent they need? Research reveals several themes, including difficulties in attracting young talent, and the need for more strategic recruitment and retention practices.
Addressing skills shortages through apprenticeships
Apprenticeships are proving to be highly effective in bridging the manufacturing skills gap, with 74% of manufacturing organisations already using these programs to introduce new talent into the industry. Combining theoretical learning with practical application, apprenticeships allow younger workers to earn a recognised qualification while being employed. What’s more, apprenticeships can be used to upskill existing staff, effectively mitigating the skills gap while ensuring a steady pipeline of talent.
Attracting and retaining EU/international skilled workers
Post-Brexit immigration policies have tightened the talent pool. Combined with the lack of awareness of manufacturing careers among younger people and an ageing workforce, the pool has become shallower and more competitive.
Manufacturers can address this issue by actively seeking skilled workers beyond traditional recruitment methods. This can be done through partnerships with overseas training providers, attending international recruitment job fairs and creating targeted online recruitment campaigns.
To help understand which roles you can focus your international recruitment initiatives, the revision of the Highly Skilled Worker Visa route and the expansion of the Shortage Occupation List, which now includes roles like production managers and engineers, are steps in the right direction.
3. Strategic workforce management for UK manufacturers
Forecasting staffing needs amid fluctuating production demands, seasonal variations and potential supply chain disruptions can be challenging. However, production and workforce management software can simplify this process. With these tools, you can track daily demand fluctuations and automatically generate optimised rotas that align with your production requirements.
Additionally, by leveraging advanced data analytics, you can identify potential skills gaps and develop targeted training plans, helping to optimise staffing levels and drive business growth.
4. Ensuring health and safety compliance in UK factories
The manufacturing environment presents unique risks, making health and safety a paramount concern. Therefore, adherence to the Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations (RIDDOR) is essential.
But ensuring compliance goes beyond one-time training. It requires establishing a robust safety culture, promoting proactive practices, and encouraging open communication between workers and management.
Integrate your health and safety data with your people data to gain a comprehensive view of the risks and incidents within your organisation. This information can then be used to identify trends, target areas for improvement and mitigate future risks. For instance, linking accident reporting with shift patterns, team dynamics, or training records can help identify root causes and develop tailored solutions to prevent future workplace risks from occurring.
It’s also crucial to have a system that checks staff compliance before scheduling staff into shifts. elementsuite’s workforce management module, for instance, prevents scheduling staff whose qualifications and certifications may have expired, and alerts employees and managers when and where updates are required.

5. Creating an engaging environment for workers
Engagement in the workplace is crucial for retaining talent and maintaining high productivity levels. This is of particular importance in the manufacturing industry, which loses approximately £7 billion per year due to unfilled vacancies.
But how do we engage employees in a sector fraught with manual labour and often monotonous tasks?
Flexible working arrangements
Offering flexible working arrangements, such as shift swapping, picking up extra shifts or compressed hours, can be a powerful engagement tool for manufacturers. With staff scheduling software, managers can empower employees to set their availability in advance, allowing them to accommodate personal commitments when creating rotas. This flexibility not only supports work-life balance but also helps to optimise scheduling.
In addition, job-sharing or compressed hours allow staff to rotate between roles without compromising manufacturing operations. This minimises burnout, fosters a diverse work culture and caters to individual preferences, ultimately contributing to a more engaged and productive workforce.
Finally, cross-training enhances team versatility by preparing employees to handle various tasks. For example, when a line operator is trained on multiple machines, they can step in for an absent colleague, keeping the assembly line running smoothly. This flexibility eases individual workloads, boosts job satisfaction, and helps reduce employee turnover in the long run.
6. Promoting diversity and inclusion in British manufacturing
The manufacturing sector faces significant diversity challenges. Although women make up approximately half of the UK’s working population, research shows that they represent a mere 26.1% of the manufacturing workforce. Similarly, ethnic minority groups account for just 13% of the sector’s workforce. To address these disparities, it is crucial to implement diversity initiatives, particularly within factory and leadership roles.
But what do these initiatives look like in practice? One effective approach is for employers to use HR software to track recruitment, retention, and progression rates across different demographics. This data can help identify any potential biases or barriers that hinder diversity. With this insight, businesses can take targeted actions, such as adopting more inclusive recruitment strategies, offering diversity training, and implementing policies that promote an inclusive workplace culture. These initiatives not only address inequality but also drive organisational success.
7. Employee development for the future of manufacturing
As the manufacturing industry evolves, so must its workforce. As mentioned earlier, the younger generation is unaware of the potential and opportunities in manufacturing. Therefore, investing in employee development and upskilling current staff is crucial for filling skill gaps and preparing the workforce for future technological advancements.
Develop leadership capabilities for supervisors and managers
Developing leadership capabilities in supervisors and managers is not just about empowering individuals – it’s about transforming the entire workplace. By enhancing these key roles, we cultivate an environment where teams are more engaged, productive, and resilient.
HR’s expertise in employee training and development is critical in this process, offering targeted programs designed to enhance leadership skills at every level.
Upskilling for new manufacturing technologies and processes
Similarly, with the speed of technological advancements in the manufacturing industry comes the need for upskilling and reskilling their workforce to meet future demands.
For instance, incorporating predictive maintenance technology and basic equipment maintenance processes training can significantly reduce stoppages and eliminate extended shutdown periods, ensuring smoother production flows. This strategic approach to upskilling not only future-proofs the workforce against technological advancements, but also positions the company as a forward-thinking leader in the manufacturing sector.
Conclusion
As highlighted, manufacturers face numerous HR challenges, from rising employment costs and skills shortages to fluctuating labour demands. The recent 2024 Autumn Budget, which introduced significant employment and tax ramifications, underscores the importance of strategic HR practices in navigating economic pressures.
Through balancing cost-control measures with forward-looking investments in technology, manufacturers can position themselves for long-term success.
Check out our Manufacturing page or book a demo with us today and discover how elementsuite can revolutionise your HR strategy for the better.




